Introduction
Autonomous vehicles, or self-driving cars, are poised to revolutionize the transportation industry. With rapid advancements in technology, these vehicles promise to enhance safety, improve efficiency, and transform the way we travel. However, the journey toward widespread adoption is fraught with challenges, including regulatory hurdles and public acceptance. This article explores the latest developments in self-driving car technology, the regulatory challenges they face, and their potential impact on the future of transportation.
Developments in Self-Driving Car Technology

Advanced Sensors and AI
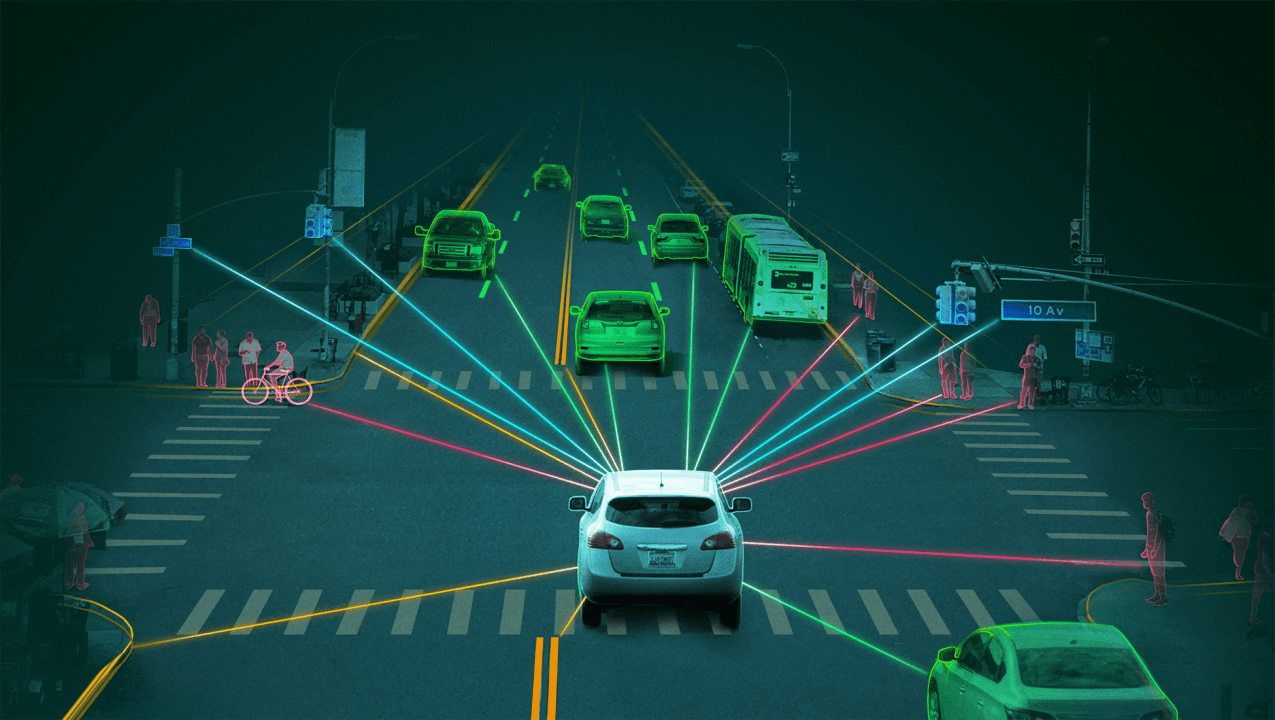
Self-driving cars rely on a combination of sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence (AI) to navigate and make decisions in real-time.
- Lidar and Radar: These sensors provide precise measurements of the vehicle’s surroundings, allowing for accurate detection of obstacles, pedestrians, and other vehicles.
- Cameras: High-resolution cameras offer a visual understanding of the environment, essential for tasks like lane-keeping and traffic sign recognition.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI algorithms process the data collected by sensors to make split-second decisions, learning from vast amounts of driving data to improve performance over time.
Software Integration
The integration of software systems is crucial for the functionality of autonomous vehicles.
- Mapping and Navigation: Advanced mapping systems provide detailed, up-to-date information about road conditions and traffic patterns.
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication: This technology allows vehicles to communicate with each other and with infrastructure like traffic lights, enhancing safety and efficiency.
Electric and Hybrid Powertrains
Many autonomous vehicles are being developed with electric or hybrid powertrains, aligning with global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable transportation.
- Battery Technology: Improvements in battery technology are extending the range and reducing the charging time for electric vehicles.
- Energy Efficiency: Autonomous driving systems optimize energy use, further enhancing the efficiency of electric and hybrid vehicles.
Regulatory Challenges
Safety Standards and Testing
Ensuring the safety of autonomous vehicles is a primary concern for regulators.
- Safety Protocols: Developing comprehensive safety protocols for testing and deployment is essential to protect passengers and pedestrians.
- Certification Processes: Establishing standardized certification processes to verify the safety and reliability of self-driving systems is crucial.
Legal and Liability Issues
The legal landscape for autonomous vehicles is complex and still evolving.
- Liability Framework: Determining liability in the event of an accident involving an autonomous vehicle presents significant challenges.
- Data Privacy: Ensuring the privacy and security of data collected by autonomous vehicles is a critical regulatory issue.
Infrastructure and Connectivity
The successful deployment of autonomous vehicles depends on robust infrastructure and connectivity.
- Smart Infrastructure: Upgrading existing infrastructure to support autonomous vehicles, such as smart traffic lights and dedicated lanes, is necessary.
- 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks will enhance the real-time data exchange required for autonomous vehicle operations.
The Future of Transportation

Urban Mobility
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to transform urban mobility by reducing congestion and improving accessibility.
- Ride-Sharing Services: Self-driving cars could lead to more efficient and affordable ride-sharing services, reducing the need for private vehicle ownership.
- Public Transportation Integration: Integrating autonomous vehicles with public transportation systems could create seamless, multimodal transportation networks.
Economic and Environmental Impact
The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles could have significant economic and environmental benefits.
- Job Creation and Transformation: While autonomous vehicles may displace certain jobs, they will also create new opportunities in technology development, maintenance, and logistics.
- Reduced Emissions: The transition to electric and hybrid autonomous vehicles could significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Rural and Long-Distance Travel
Autonomous vehicles can enhance mobility and accessibility in rural areas and for long-distance travel.
- Improved Accessibility: Self-driving cars can provide reliable transportation options for individuals in rural or underserved areas.
- Efficient Logistics: Autonomous trucks and delivery vehicles can optimize long-distance travel and logistics, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Conclusion
Autonomous vehicles represent a transformative shift in transportation, offering the potential for safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly travel. However, the path to widespread adoption involves navigating complex regulatory challenges and ensuring public acceptance. By staying informed about the latest developments and regulatory landscapes, stakeholders can help shape the future of transportation. The ongoing advancements in self-driving car technology promise to make autonomous vehicles an integral part of our daily lives in the near future.